The global urgency for alternative energy solutions to combat the escalating climate crisis is undeniable. Numerous proposals aiming to harness energy from renewable sources have been put forth, varying in their practicality and viability. Tidal energy stands out as a particularly promising option, alongside wind and solar power, owing to its reliability and the vast expanse of the oceans. Moreover, its potential impact extends beyond mere energy generation, with the capacity to enhance the quality of life for urban dwellers and inhabitants of remote, underserved communities worldwide.
An In-Depth Look at Tidal Power
Tidal power, in essence, refers to the process of harnessing energy from tides, a practice primarily aimed at generating electricity. This type of renewable energy is intriguing due to its predictable nature. The gravitational forces of the moon and the sun, interacting with the Earth’s rotation, give rise to tides. The strength and dimensions of these tides, however, fluctuate globally.
Tidal power has a historic foundation dating back over a millennium, with evidence of its use in the form of tide mills across Europe and North America. These tide mills worked by allowing water to accumulate in large ponds. The subsequent outflow of water would then turn waterwheels, converting kinetic energy into mechanical power. These mills were often strategically positioned on grain farms, where their mechanical power proved instrumental in processing the harvest.
Strengthening our understanding of tidal power and its applications can offer insights into how this renewable energy might be utilized as part of our sustainable future. Here’s a closer look at some of its implications:
- Predictability: Unlike other renewable energy sources that can be somewhat erratic, tidal power boasts remarkable predictability. This consistency can be attributed to the predictable cycle of tides caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun. This feature makes tidal an ideal candidate for reliable power generation;
- Historical Precedent: For centuries, mankind has utilized the power of the tides, implementing systems such as the tide mills of Europe and North America. This history demonstrates that harnessing tidal power is not only possible but proven and effective;
- Global Variation: The strengths and dimensions of tides can differ from one geographical location to another. As such, the potential for tidal power generation will also vary globally. Understanding these variations can help identify regions with the greatest potential for exploiting this renewable energy resource.
UNESCO asserts that tidal energy could provide as much as 12% of the world’s current power needs. The challenge lies in developing efficient, cost-effective technologies to harness this vast yet under-utilized resource.
Delving into the Core Types of Tidal Power Systems
Harnessing the power of the ocean’s tides is no small feat. Several innovative systems have been developed for this purpose. Primary among these are the tidal barrage, the tidal turbine, and the tidal fence. Each of these systems boasts unique features that make them particularly suited to capturing energy from the tides.
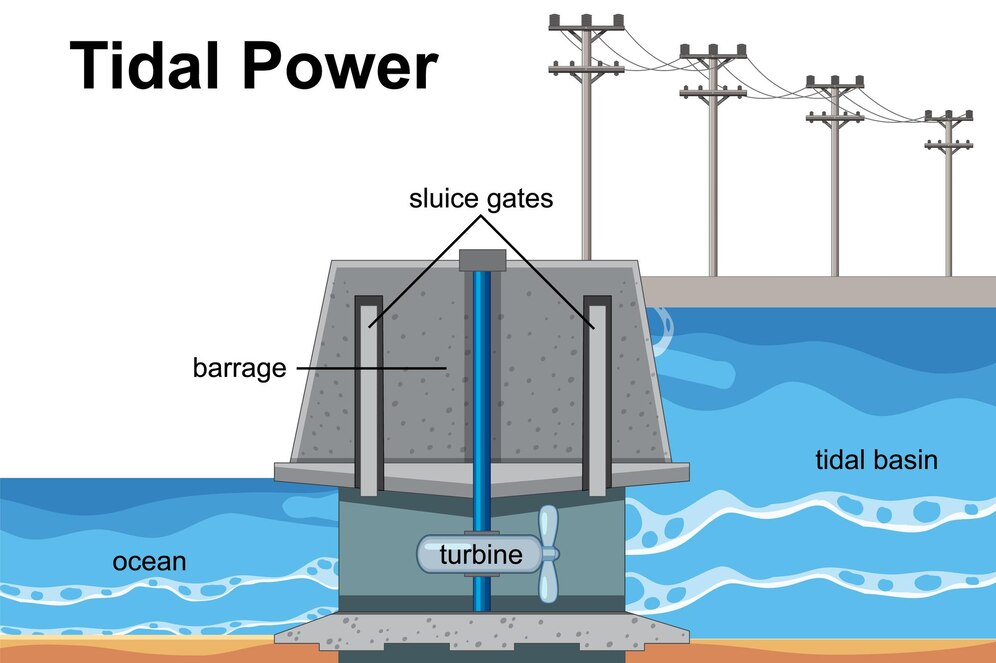
Tidal Barrage
Picture a structure similar to a dam, and you’ve essentially visualized a tidal barrage. Its strategic position across the mouths of oceans or lagoons allows it to effectively adapt to water flow rates via sluice gates. One of its most commendable features is its two-way tidal power system which produces electricity from incoming and outgoing tides.
Key points to remember about tidal barrages include:
- These structures resemble dams and are usually installed across ocean lintels or lagoons;
- They use sluice gates to regulate water and flow rates;
- Their two-way system creates electricity from both incoming and outgoing tides.
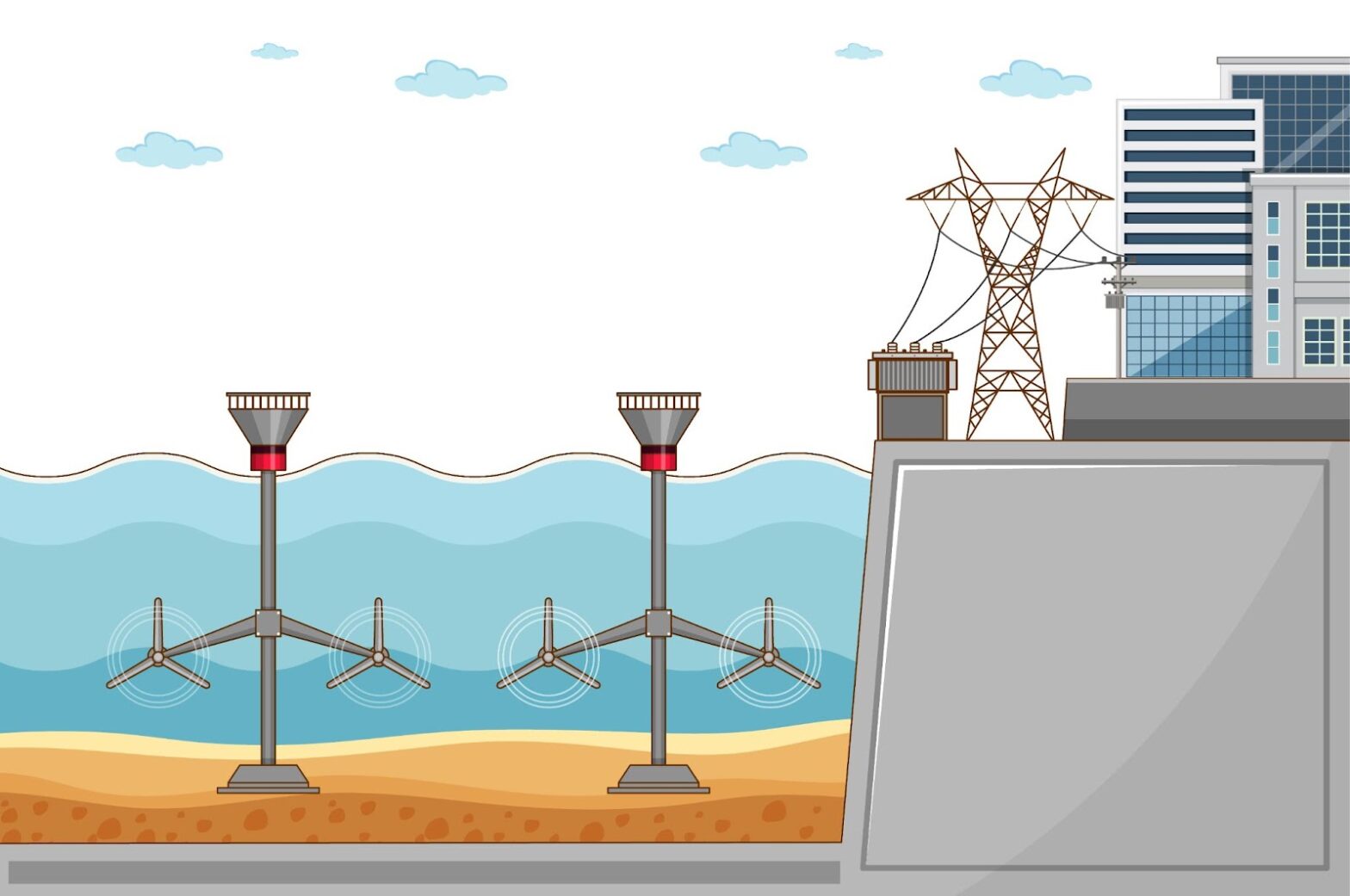
Tidal Turbine
Think of a wind turbine, then imagine it on the sea floor in an area with powerful tides. This is essentially a tidal turbine. These robust devices come with a hefty price tag due to the advanced technology and materials required to withstand harsh marine conditions and generate electricity efficiently.
Noteworthy aspects of tidal turbines entail:
- They are usually located on the sea floor in areas with strong tides;
- Constructing a tidal turbine often demands a substantial investment given their intricate structure and the need for durable, high-tech materials.
Tidal Fence
Envision a network of vertical axis turbines settled on the seabed. As water rushes through these turbines, electricity is generated. This arrangement is known as a tidal fence. The Energy Information Administration (EIA) details how this system leverages the kinetic energy of tides.
Key insights on tidal fences include:
- They comprise a series of vertical axis turbines affixed to the seabed;
- As water flows through these turbines, it helps generate electricity.
Understanding the functioning and unique features of these tidal power systems can offer crucial insights into the potential and feasibility of tidal energy as a sustainable power source.
Current Application of Tidal Power
While tidal power isn’t as prevalent as other forms of renewable energy, it holds immense untapped potential. Scientists and energy experts recognize this potential, but significant harnessing of tidal energy is yet to be realized extensively.
At present, several tidal power plants are operational around the world. Let’s delve into their geographical distribution and energy outputs:
Noteworthy Tidal Power Plants
- South Korea: Sihwa Lake Tidal Power Station: The largest in the world, with a generation capacity of 254 megawatts. This impressive installation demonstrates the power and potential of this energy source;
- France: Rance Tidal Power Station: Located on the estuary of the Rance River, this power station was the first to connect to the grid. Its long-standing operation since 1966 attests to tidal power’s reliability;
- Canada: Annapolis Royal Generating Station: Found in Nova Scotia, this plant is the third largest of its kind, capable of generating 20 megawatts of energy. It exemplifies the feasibility of tidal power, even in regions with less aggressive tides;
- Russia: Kislaya Guba Tidal Power Station, the first tidal power station in Russia and the second oldest tidal power plant in the world;
- China: Jiangxia Tidal Power Station: Producing a power capacity of 3.9 MW, this plant underscores the role of tidal power in a diversified energy portfolio.
Regrettably, tidal power hasn’t been exploited to its full potential in the United States. This lack of development is partially attributable to insufficient financial commitment to the technology and a dearth of sites presenting the ideal conditions for economically-viable tidal power generation.
This current landscape of tidal power usage is rapidly changing. As technology advances and the dire need for sustainable energy sources becomes more apparent, tidal power promises to be an increasingly important player in the global energy scene.
Harnessing The Advantages of Tidal Power
Tidal power is a promising alternative energy source due to its numerous assets. This renewable energy form is vital in our quest for cleaner, sustainable power generation. Here, we delve into its diverse benefits and how they stack up against other renewable energy sources.
Environmental Sustainability
Tidal power stands out for its cleanliness. As a natural renewable energy source, it contributes towards curbing our reliance on fossil fuels such as coal and oil. This independence from non-renewable energy correlates directly with reduced carbon emissions, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
Predictability
Tidal power trumps other renewable energy sources like wind and solar power when it comes to predictability. Tides occur in regular cycles due to the gravitational pull of the moon and sun, making tidal power a more consistent and reliable energy source.
Potentially Abundant Power Generation
A study by the US National Renewable Energy Laboratory indicates that tidal power could theoretically cater to a significant portion of America’s electricity needs, potentially up to a third. Such abundance underlines the capacity of tidal energy to become a significant contributor to the national energy mix.
Scalability
Tidal power technology can be tailored to various scales and corresponding cost-points, making it a versatile solution for diverse energy needs. Its applicability ranges from remote communities to bustling cities. A noteworthy example is the Ocean Renewable Power Company’s project in Alaska’s Kvichak watershed, where local communities benefit from an established tidal power system.
These advantages make tidal power an increasingly attractive proposition for a sustainable energy future. As technology progresses and the efficiency of tidal power systems improves, we can anticipate a broader adoption of this promising energy resource.
Unveiling the Challenges of Tidal Power
Despite its potential, tidal power isn’t without challenges. Various factors have limited its widespread adoption, notwithstanding its theoretical capabilities. An understanding of these challenges provides perspective and helps shape realistic strategies for tidal power integration.
Cost-Intensity
Tidal power’s high initial cost compared to other renewable energy sources serves as a deterrent to its wider use. However, it should be noted that while the upfront costs are high, the long-term operational costs are significantly lower due to minimal maintenance and running costs.
Limited Suitable Sites
Suitable sites for tidal power generation are relatively rare. To be effective, tidal ranges should be at least ten feet, which restricts the geographical applicability of this energy form. Technological advancements may, however, provide solutions to this limitation in the future.
Potential Ecological Impact
Tidal power stations can necessitate large-scale constructions that may impact an area’s ecosystem. The changes in tidal levels and turbidity can affect marine animal navigation and disrupt aquatic plant life. Thorough environmental impact assessments are crucial to ensure responsible development of tidal power facilities.
Despite these challenges, tidal power holds promise. As technological advancements continue to make the process more cost-effective and expand the potential sites for power collection, tidal power could become a more significant contributor to the world’s clean energy mix. Policymakers, scientists, and societies must remain open to the potential of tidal power, exploring realistic ways to harness its benefits while minimizing its drawbacks.
The Rising Tide: Innovations Boosting Tidal Energy’s Potential
The dawn of a new era in tidal power is upon us, fuelled by relentless innovation from numerous energy companies. According to Yale Environment 360, an impressive array of 30 tidal and 40 wave energy firms are making significant strides in improving the viability and effectiveness of tidal power.
This surge of vibrant innovation is revolutionizing the industry, with advances promising economical and eco-friendly solutions. Modern tidal power systems are slowly being perfected to operate without disturbing surrounding marine ecosystems. Yale Environment 360 anticipates that the future of tidal energy will be largely dependent on strategically installed sea-bottom or floating turbines, which can harness the immense energy from ocean currents in an eco-friendly manner.
Companies across the globe are at the forefront of these ground-breaking developments. French firm DCNS, Carnegie Wave Energy in Australia, and Hawaii-based Azura are just a few of the entities championing ingenious new systems. An exciting example is a grid array composed of 240-kilowatt buoys developed by Carnegie Wave Energy, marking a significant leap in the tidal power sector.
Other innovative offerings include the deployment of axial turbines, reminiscent of underwater windmills and the utilization of tidal stream generators, which extract energy from moving tides with minimal environmental impact.
These accelerating breakthroughs imply a promising future where tidal power is economically competitive with solar and wind energy. As more efficient and environmentally conscious tidal energy solutions emerge, tidal power’s role in the global energy landscape seems destined to grow. It is increasingly clear that tidal power is poised to become a key player in our journey towards a sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pressing need for alternative energy solutions in response to the looming climate crisis cannot be overstated. Tidal energy emerges as a compelling option among the array of renewable sources, offering not only reliability but also the potential to positively impact both urban centers and remote communities. As we continue to explore and invest in such sustainable technologies, we move closer to a future that is both environmentally sound and socially equitable.